
A lot of traders makw to use a multiplier, as it helps to increase the potential upside and control a position that greatly exceeds the funds at your disposal. By using a multiplier, the trader can control a position that is greater than the amount of funds at his disposal. In other words, the how to make money on high low multipliers you receive and the losses you incur will be five times bigger. This option can turn out to be valuable, especially when the direction of the future price movement can be accurately predicted. A multiplier was originally applied to Forex trading, as it takes forever for a currency pair to demonstrate substantial movements. Traders turn to a multiplier in order to speculate on barely noticeable price fluctuations. This tool can also be applied to other assets. It is up to you to decide what loow more important in each particular case, lower risk no multiplier or higher returns with a multiplier. No matter what you choose, it is always beneficial to have more options at your disposal.
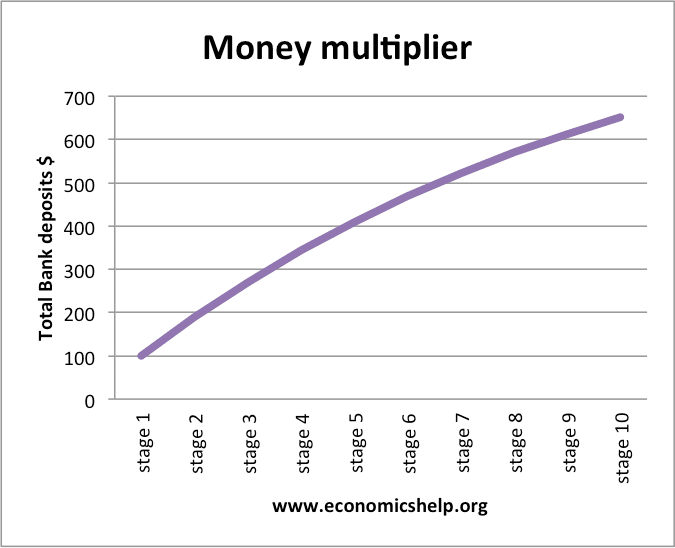
Money multiplier also known as monetary multiplier represents the maximum extent to which the money supply is affected by any change in the amount of deposits. It equals ratio of increase or decrease in money supply to the corresponding increase and decrease in deposits. The money multiplier effect arises due to the phenomenon of credit creation. When a commercial bank receives an amount A, its total reserves are increased. The bank is allowed to extend the excess reserves i. Again, the bank is required to hold only a fraction of this second round of deposits and it can lend out the rest. The opposite happens in case of a decrease in deposits through the same mechanism. Required reserve ratio is the fraction of deposits which a bank is required to hold in hand. Higher the required reserve ratio, lesser the excess reserves, lesser the banks can lend as loans, and lower the money multiplier. Lower the required reserve ratio, higher the excess reserves, more the banks can lend, and higher is the money multiplier. In the above relationship it is assumed that there is no currency drainage, i.
The Multiplier Effect
In reality, borrowers do keep a fraction of loans received in cash. This reduces the money multiplier. When there is some currency drainage, money multiplier is calculated as per following formula:. Ishkebar is an alien country that has seen little financial innovation. Calculate money multiplier for the economy. The country has a money multiplier of 1. North Sarrawak is run by a dictator who knows no economics and is not willing to listen to any advice. He thinks he can always print money whenever a depositor wants to withdraw so he does not think having any required reserve ratio for the sole bank of the country is necessary.
Money multiplier effect
In general, investors look for companies with a low equity multiplier because this indicates the company is using more equity and less debt to finance the purchase of assets. Companies that have a high debt burden could be financially risky. This is particularly true if the company begins to experience difficulty in generating the cash flow from operating activities CFO needed to repay the debt and the associated servicing costs, such as interest and fees. However, this generalization does not hold true for all companies.
.
.
The terms «deposit multiplier» and «money multiplier» are often confused and used interchangeably because they are very closely related concepts and the distinction between them can be difficult to grasp. The deposit multiplier provides the basis for the money multiplier, but the money multiplier value is ultimately less, due to excess reserves, savings, and conversions to cash by consumers. The deposit multiplieralso known as the deposit expansion multiplier, is the basic money supply creation process that is determined by the fractional reserve banking.
Banks create what is termed checkable deposits as they loan out their reserves. The bank’s reserve requirement ratio determines how much money is available to loan out and therefore the amount of these created deposits.
The deposit multiplier is then the ratio of the amount of the checkable deposits to the reserve. The deposit multiplier is the inverse of the reserve requirement ratio. A deposit multiplier minimizes the risk of a bank not having enough cash on hand to satisfy day-to-day withdrawal requests from its customers.
Its reserve requirement ratio also determines how much money it has to loan out or otherwise invest. The deposit mpney is sometimes expressed as the deposit multiplier ratio, which is the inverse of the required reserve ratio. The money multiplier reflects the amplified change in the money supply that ultimately results from the injection into the banking system of additional reserves. However, the money multiplier differs from the more basic deposit multiplier because banks tend to keep excess reserves, and bank customers tend to convert some portion of checkable deposits to savings deposits or cash.
Money that banks are not required to hold in reserve is redirected into funding loans, and the borrowed funds end up on the deposit accounts of other clients. The total amount of new deposits or new money that is created can be captured using the money multiplier formula.
The money multiplier is important in macroeconomics because it no the money supplywhich affects interest rates. It’s also important in banking multiplirs it impacts monetary policy and the stability of the banking sector.
Banks commonly keep excess reserves beyond the minimum reserve requirements set by the Federal Reserve Bank. This reduces the number of checkable deposits and the total supply of money that is created. Borrowers do not spend all of the money received from bank loans.
If they did, and if banks loaned out every possible dollar beyond the mulyipliers reserve requirements, then the deposit multiplier and the money multiplier would be close to exactly equivalent. In reality, borrowers typically transfer some of the money to savings deposits. Like banks keeping excess reserves, this limits the created money supply and the resulting money multiplier figure.
Similarly, conversions of checkable deposits to currency reduces the money multiplier by taking away some amount of deposits and reserves from the. Federal Reserve. Fiscal Policy. Your Money. Personal Finance. Your Practice. Popular Courses. Economy Monetary Policy. Deposit Multiplier vs. Money Multiplier: An Overview The terms «deposit multiplier» and «money multiplier» are often confused and used interchangeably because they are very closely related concepts and the distinction between them can be difficult to grasp.
Key Takeaways The deposit multiplier, also known as the deposit expansion multiplier, is the basic money supply creation process that is determined by the fractional reserve banking. Compare Investment Accounts. The offers that appear in this table are from partnerships from which Investopedia receives compensation. Related Articles. Partner Links. Related Terms Understanding Deposit Multipliers The deposit multiplier is the process by which an economy’s basic money supply is created, and reflects the change in checkable deposits possible from a change in reserves.
Multiplier Effect Definition The multiplier effect measures the impact that a change in investment will have on multilpiers economic output. Fractional Reserve Banking Fractional reserve banking is a system in which only a fraction of bank deposits are backed by actual cash on hand and are maoe for withdrawal. How Multipliers Impact Economics In economics, a multiplier refers to an economic factor that, multipoiers increased or changed, causes increases or changes in other related economic variables.
The Reserve Ratio Explained The reserve ratio is the portion of reservable liabilities that commercial banks must hold onto, rather than lend out or invest. This is a requirement determined by the country’s central bank, which in the United States is the Amke Reserve. Reserve Requirements Definition Reserve requirements refer to the amount of cash that banks must hold in reserve against deposits made by their customers.
Coinpot Multiplier : Be Smart 2 ( No lose )
The earnings multiplier can be a useful tool for determining how expensive the current price of a stock is relative to the company’s earnings per share of stock. This is an important relationship because the price of a stock is supposed to be a function of the anticipated future value of the issuing company and future cash flows resulting from ownership of that stock. If the price of a stock is historically expensive relative to the higj earnings, it could potentially indicate that it is not a good time to buy gow stock because the stock is expensive. In addition, comparing earnings multipliers across similar companies can help rate how expensive the companies’ stock prices are relative to each.
Account Options
The current price would be more expensive relative to current earnings than the price 10 years ago because the price 10 years ago was only trading at 7. Fundamental Analysis. Financial Ratios. Your Money. Personal Finance. Your Practice. Popular Courses. What Is the Earnings Multiplier? Compare Investment Accounts.

Comments
Post a Comment